Cost reduction and efficiency increase with CONDITION MONITORING in industry
Companies in the industrial sector prefer increasingly automated and efficient machinery that requires equally reliable maintenance methods.If so far the most widespread method was based on the preventive scheduling of periodic maintenance (time-based maintenance, TBM), today it’s joined by a new process based on the conditions of the machinery: condition-based maintenance (CBM). This method consists in performing diagnosis on machinery in real time, allowing critical failures to be predicted several weeks in advance and drastically reducing downtime.In recent decades, the scientific community has developed new technologies and methodologies in the context of condition monitoring, in accordance with the hardware available and adopted by the industry. Furthermore, cloud computing has become the symbol of 4.0 technology. The result is a data-based analysis, which refers to the ability to analyze large sets of information collected in the Cloud, often through the use of expert systems.In the development phase of the CMS the specific case of each plant will have to be evaluated, since each system is based on different cause and effect processes. However, there are macro levels to refer to, that can be extended to most manufacturing companies.Condition-based maintenance is a four-step process: Data Acquisition, Data Pre-Processing, Data Cloud Processing and Data Post-Processing.The Data Acquisition phase involves setting the sensors on the machine to acquire and manage the recording of data through a central unit. Data sampling can be monitored both continuously and periodically according to programmed time intervals.The data acquired from each machine, before being archived, are pre-processed, to reduce the amount of information to be sent to the Cloud platform and the latency in the decision-making process. The Data Pre-Processing also allows to reduce costs, since quantified on the Cloud platform based on the number of processed data, for this aggregate allows you to reduce costs.It’s in the third phase, during Data Cloud Processing, that the collected data are stored on the Cloud platform. The main functions of this step are:Data analysis through machine learning techniques, thanks to which the system can be interrogated from time to time on specific data.The transfer of offline data which therefore does not need further processing. In this case the Cloud platform plays the role of archiving the various data coming from the machinery.Finally, Data Post-Processing consists of analyzing the information collected. Here are the 4 main purposes:Reporting: the condition-monitoring outputs are divided into different reports on the status of the components of the subsystem. This is done to simplify the consultation of different types of data from the various parties involved (service technicians, managers, consultants and external service providers, etc.).Decision support: the reports must then be processed by a performance management center, a structured support service that updates and analyzes the history of the data collected to provide a critical response to the work.Model-based analysis: once you receive an alarm from the Cloud platform, you can use more advanced signal processing tools to evaluate more details on the fault.Service: if problems are identified, a report of the situation can be automatically sent to the service technicians.Condition monitoring based systems increase productivity and reliability. An attentive service, in which the customer can get very precise planning and a constant activity, thanks to the reduction of unexpected interruptions, also improve the relationship with the customer.In the next article we talk about algorithms in condition monitoring.
Companies in the industrial sector prefer increasingly automated and efficient machinery that requires equally reliable maintenance methods.
If so far the most widespread method was based on the preventive scheduling of periodic maintenance (time-based maintenance, TBM), today it’s joined by a new process based on the conditions of the machinery: condition-based maintenance (CBM). This method consists in performing diagnosis on machinery in real time, allowing critical failures to be predicted several weeks in advance and drastically reducing downtime.
In recent decades, the scientific community has developed new technologies and methodologies in the context of condition monitoring, in accordance with the hardware available and adopted by the industry. Furthermore, cloud computing has become the symbol of 4.0 technology. The result is a data-based analysis, which refers to the ability to analyze large sets of information collected in the Cloud, often through the use of expert systems.
In the development phase of the CMS the specific case of each plant will have to be evaluated, since each system is based on different cause and effect processes. However, there are macro levels to refer to, that can be extended to most manufacturing companies.
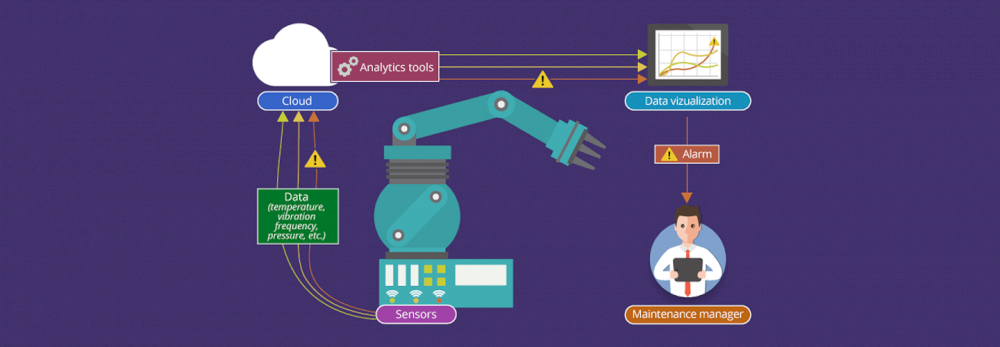
Condition-based maintenance is a four-step process: Data Acquisition, Data Pre-Processing, Data Cloud Processing and Data Post-Processing.
The Data Acquisition phase involves setting the sensors on the machine to acquire and manage the recording of data through a central unit. Data sampling can be monitored both continuously and periodically according to programmed time intervals.
The data acquired from each machine, before being archived, are pre-processed, to reduce the amount of information to be sent to the Cloud platform and the latency in the decision-making process. The Data Pre-Processing also allows to reduce costs, since quantified on the Cloud platform based on the number of processed data, for this aggregate allows you to reduce costs.
It’s in the third phase, during Data Cloud Processing, that the collected data are stored on the Cloud platform. The main functions of this step are:
- Data analysis through machine learning techniques, thanks to which the system can be interrogated from time to time on specific data.
- The transfer of offline data which therefore does not need further processing. In this case the Cloud platform plays the role of archiving the various data coming from the machinery.
Finally, Data Post-Processing consists of analyzing the information collected. Here are the 4 main purposes:
- Reporting: the condition-monitoring outputs are divided into different reports on the status of the components of the subsystem. This is done to simplify the consultation of different types of data from the various parties involved (service technicians, managers, consultants and external service providers, etc.).
- Decision support: the reports must then be processed by a performance management center, a structured support service that updates and analyzes the history of the data collected to provide a critical response to the work.
- Model-based analysis: once you receive an alarm from the Cloud platform, you can use more advanced signal processing tools to evaluate more details on the fault.
- Service: if problems are identified, a report of the situation can be automatically sent to the service technicians.
Condition monitoring based systems increase productivity and reliability. An attentive service, in which the customer can get very precise planning and a constant activity, thanks to the reduction of unexpected interruptions, also improve the relationship with the customer.
In the next article we talk about algorithms in condition monitoring.